When you’re learning TypeScript, you might come across the term “default” in the context of modules. In this Typescript tutorial, I will explain what is the Typescript default keyword and how to use the default keyword in Typescript with a few practical examples.
The default keyword in Typescript is used for exporting a single value (like a function, class, or variable) from a module, making it the main export. This simplifies imports in other files, allowing you to import this value without specifying its name. It’s especially useful when a module primarily aims to provide one specific functionality.
What is the “default” Keyword in Typescript?
In TypeScript, the “default” keyword is used during module export to specify a default export. Unlike named exports, a default export allows a module to export a single value, which can be a function, a class, or a variable. This makes imports more concise and is particularly useful when a module is designed to export one main functionality.
Why Use Default Exports in Typescript?
Here are a few reasons why we use the default exports in Typescript.
- Simplicity: Default exports simplify the import syntax when only one value is being exported.
- Readability: It improves readability, making the primary functionality of the module clear.
- Flexibility: Allows renaming of the imported value without an additional import syntax.
Typescript default keyword syntax
Here is a syntax for exporting a default value in Typescript.
// Exporting a function as default
export default function greet(name: string): string {
return `Hello, ${name}!`;
}
// Exporting a class as default
export default class User {
constructor(public name: string) {}
}
// Exporting a variable as default
const greeting = "Hello World";
export default greeting;
Below is how you can import a default export in Typescript.
// Importing a default-exported function
import greet from './greet';
// Importing a default-exported class
import User from './User';
// Importing a default-exported variable
import greeting from './greeting';
default Keyword in Typescript Examples
Now. let us check some examples to understand how to use the default keyword effectively.
Example 1: Default Function Export
greet.ts
export default function greet(name: string): string {
return `Hello, ${name}!`;
}
app.ts
import greet from './greet';
console.log(greet('Alice'));
You can see the output in the screenshot below once you run the code using Visual Studio Code.
To run the above Typescript code, run the below two commands:
tsc app.ts
node app.js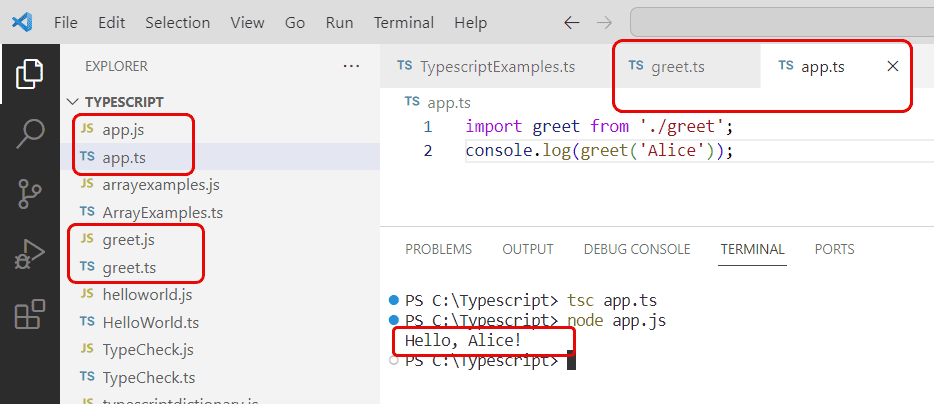
Example 2: Default Class Export
User.ts
export default class User {
constructor(public name: string) {}
}
app.ts
import User from './User';
const user = new User('Bob');
console.log(user.name); // Output: Bob
Example 3: Default Variable Export
constants.ts
const greeting = "Welcome to TypeScript";
export default greeting;
app.ts
import greeting from './constants';
console.log(greeting); // Output: Welcome to TypeScript
Conclusion
In TypeScript, the “default” keyword is used for exporting a single value (like a function, class, or variable) from a module, making it the main export. In this tutorial, we understood:
- What is the “default” Keyword in Typescript?
- Why Use Default Exports in Typescript?
- Typescript default keyword syntax
- default Keyword in Typescript Examples
You may also like:
I am Bijay a Microsoft MVP (10 times – My MVP Profile) in SharePoint and have more than 17 years of expertise in SharePoint Online Office 365, SharePoint subscription edition, and SharePoint 2019/2016/2013. Currently working in my own venture TSInfo Technologies a SharePoint development, consulting, and training company. I also run the popular SharePoint website EnjoySharePoint.com