Recently, I got a requirement to filter an array of objects in PowerShell. I checked a few methods, and in this PowerShell tutorial, I will explain how to filter an array of objects in PowerShell using various methods.
To filter an array of objects in PowerShell, you can use the Where-Object cmdlet, which allows you to specify conditions for filtering. For example, $array | Where-Object { $_.PropertyName -eq “Value” } filters objects where the property “PropertyName” equals “Value”. Alternatively, the .Where() method can be used on the array directly, such as $array.Where({ $_.PropertyName -eq “Value” }), which offers a more efficient, pipeline-free way to achieve the same result.
Arrays of Objects in PowerShell
Let’s understand what an array of objects is. In PowerShell, an array is a data structure that can hold multiple items. These items can be of any data type, including objects. An object in PowerShell is an instance of a class that can contain properties and methods. When we talk about an array of objects, we mean a collection of instances we can manipulate as a group.
Filter Array of Objects in PowerShell Using the Where-Object Cmdlet
The most common way to filter an array of objects in PowerShell is by using the Where-Object cmdlet. This cmdlet allows you to specify criteria to filter objects. The objects that meet the conditions of the filter are then passed down the pipeline or stored in a variable.
Basic Syntax of Where-Object
$array | Where-Object { $_.PropertyName -Operator Value }$arrayis the array of objects you want to filter.$_represents the current object being processed in the pipeline.PropertyNameis the name of the property you want to filter on.Operatoris the comparison operator (e.g.,-eqfor equals,-gtfor greater than).Valueis the value you want to compare the property to.
Example: Filtering an Array of Custom Objects in PowerShell
Let’s create an array of custom objects and then filter it in PowerShell.
# Create an array of custom objects
$people = @(
@{Name='Alice'; Age=30},
@{Name='Bob'; Age=25},
@{Name='Charlie'; Age=35}
) | ForEach-Object { New-Object PSObject -Property $_ }
# Filter the array to find people older than 30
$olderThan30 = $people | Where-Object { $_.Age -gt 30 }
# Display the filtered objects
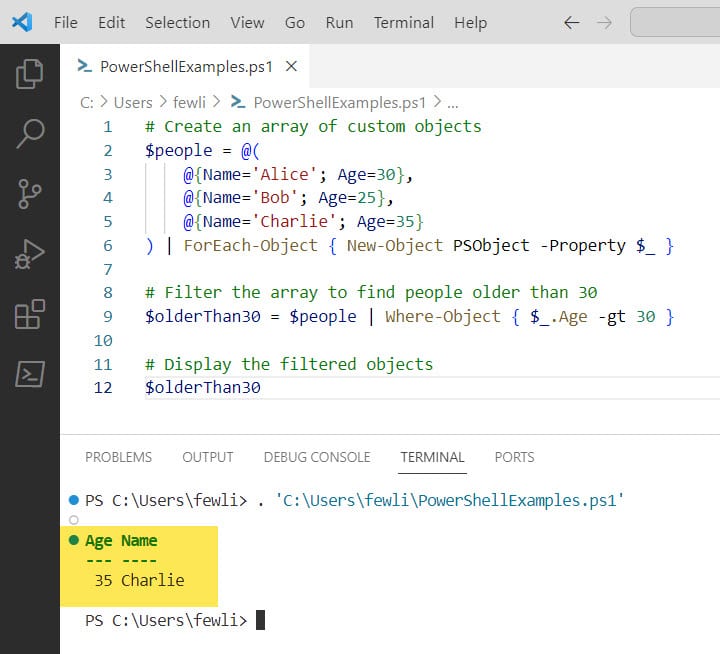
$olderThan30In this example, we first create an array of custom objects $people with properties Name and Age. We then use Where-Object to filter out the people who are older than 30 and store the results in $olderThan30.
Once you run the PowerShell script, you can see the output in the screenshot below:
Filter Array of Objects in PowerShell Using the .Where() Method
PowerShell also provides a .Where() method that you can use to filter objects in an array. This method is often faster than Where-Object because it does not involve the pipeline.
Syntax of .Where() Method
$array.Where({ $_.PropertyName -Operator Value })Example: Using .Where() to Filter Objects
Let’s use the same array of people and filter an array of objects in PowerShell using the .Where() method.
# Create an array of custom objects
$people = @(
@{Name='Alice'; Age=30},
@{Name='Bob'; Age=25},
@{Name='Charlie'; Age=35}
) | ForEach-Object { New-Object PSObject -Property $_ }
# Filter the array to find people younger than 30
$youngerThan30 = $people.Where({ $_.Age -lt 30 })
# Display the filtered objects
$youngerThan30Here, we filter the $people array to find people younger than 30 using the .Where() method and store the result in $youngerThan30.
Filter Array of Objects in PowerShell with Multiple Conditions
Both Where-Object and .Where() can be used to filter an array of objects in PowerShell with multiple conditions.
# Create an array of custom objects
$people = @(
@{Name='Alice'; Age=30},
@{Name='Bob'; Age=25},
@{Name='Charlie'; Age=35}
) | ForEach-Object { New-Object PSObject -Property $_ }
# Filter the array for people named 'Alice' or older than 32
$aliceOrOlderThan32 = $people | Where-Object { $_.Name -eq 'Alice' -or $_.Age -gt 32 }
# Display the filtered objects
$aliceOrOlderThan32In this example, we use a script block with -or to filter for people named ‘Alice’ or older than 32.
Conclusion
Filtering an array of objects in PowerShell can be possible using the Where-Object cmdlet or the .Where() methods.
In this PowerShell tutorial, I have explained how to filter an array of objects in PowerShell.
You may also like:
- How To Compare Array Of Objects In PowerShell?
- How to Access Array of Objects in PowerShell?
- How To Format An Array Of Objects As Table In PowerShell?
- How to Merge Two Objects in TypeScript?
I am Bijay a Microsoft MVP (10 times – My MVP Profile) in SharePoint and have more than 17 years of expertise in SharePoint Online Office 365, SharePoint subscription edition, and SharePoint 2019/2016/2013. Currently working in my own venture TSInfo Technologies a SharePoint development, consulting, and training company. I also run the popular SharePoint website EnjoySharePoint.com